Cirrhosis can be diagnosed with ultrasound CT and MRI and these imaging modalities can also be used to evaluate for possible complications of cirrhosis such as portal hypertension or hepatocellular carcinoma. It facilitates metabolism and improves the breakdown of many substances.
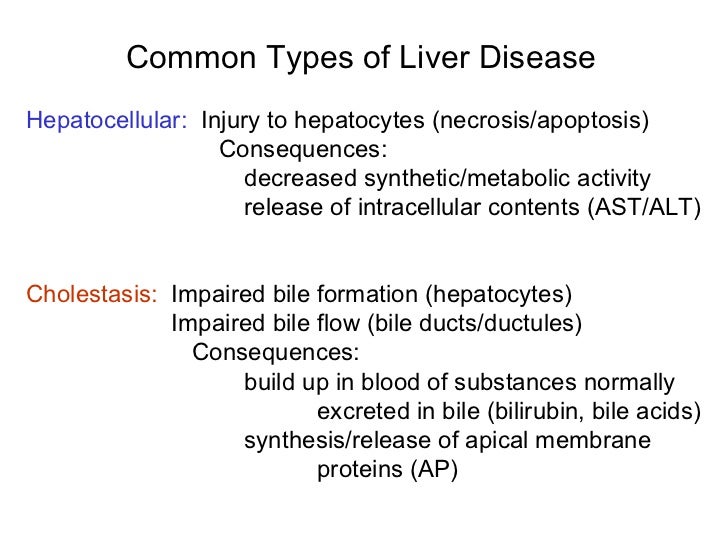 02 02 12 Hepatocellular Disease
02 02 12 Hepatocellular Disease
The goal of treatment is to slow down the buildup of scar tissue and prevent or treat any problems that happen.

Chronic hepatocellular disease. Yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes. In this article we explore different types of chronic liver diseases common causes for chronic liver disease the symptoms of chronic liver disease and tips for managing liver disease. The classic symptoms of diffuse hepatocellular liver disease include.
Hepatocellular carcinoma HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. We assessed incidence and predictors of HCC by a systematic review and meta-analysis. Autoimmune hepatitis Injury to normal hepatocytes by infiltrating T cells and plasma cells leading to fibrosiscirrhosis Lab tests.
Anti-nuclear antibodies Anti-smooth actin muscle antibodies High level of polyclonal immunoglobulins IgG Chronic disease but usually highly response to suppression by prednisone and azathioprine. Distension of the abdomen. The damage to the liver usually cant be reversed.
Hepatocellular Disease also known as Wilsons disease is a rare and inherited disorder of copper metabolism in which copper accumulates slowly in the liver and is then released and taken up in other parts of the bodyHemolysis then Hemolytic anemias occur as the copper accumulates in. Hepatocellular disease of the liver may either be an infection of the liver or cancer of the liver. Hepatocellular carcinoma HCC is the most common type of primary liver cancer.
While its considered a rare disease in the United States HCC is responsible. Hepatocellular carcinoma is a cancer that starts in your liver. It is located just below the right rib cage and stands as the powerhouse or the engine of the body.
At their most advanced stage CLDs often lead to the development of cirrhosis defined as the irreversible distortion of the liver architecture by fibrosis scar and abnormal nodules. Underlying chronic liver disease has been associated with an increased risk of developing HCC. Cirrhoses is the common endpoint of a wide variety of chronic liver disease processes which cause hepatocellular necrosis.
Other medical problems can also cause it. The American Liver Foundation states that alcoholism is the most common cause of cirrhosis in the. Hepatocellular carcinoma HCC is a type of liver cancer that begins in the hepatocytes the main type of liver cell.
However chronic hepatocellular disease can last for a long time and present with a variety of symptoms. Chronic liver failure is usually a result of cirrhosis or alcohol-related liver disease ARLD. We included longitudinal studies and randomized controlled trials assessing HCC incidence in untreated patients.
The liver is one of the biggest and most important organs in the body. Chronic liver disease is a condition that pursues on a continuous basis and potentially leads to complications or more severe liver conditions. Its different from secondary liver cancers which have spread to the liver from other organs.
However chronic hepatocellular disease can last for a long time and present with a variety of symptoms. Hepatocellular carcinoma occurs most often in people with chronic liver diseases such as cirrhosis caused by hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection. If caught early it can sometimes be.
The most common causes are hepatitis and other viruses and alcohol abuse. It comprises of 3 sections and 6 chapters to introduce the intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome in chronic liver diseases ascites with hyponatremia acute kidney injury portal vein thrombosis spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in liver cirrhosis and the use of stereotactic body radiation therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Chronic liver diseases CLDs are a set of diseases characterized by decreased hepatic function as a result of chronic inflammation or insult to the liver.
In the natural history of hepatitis B virus HBV chronic infection the hepatocellular carcinoma HCC risk is unclear. Cirrhosis is a long-term chronic liver disease.


