Prevention and controlling lymphedema play an important role with this condition since there is no cure. The biggest risk to not treating lymphedema is an increased risk of infection.
Lymphedema can also occur about 4 to 6 weeks after surgery or radiation and then go away over time.

Does lymphedema go away. However it is believed that an early diagnosis and treatment of any temporary swelling can help prevent chronic lymphedema from happening. Still there are many people who have mild lymphedema that goes away with treatment and never becomes a major problem. Lymphedema occurs after several lymph nodes are removed or in the natural absence or impairment of them.
The main symptom of lymphoedema is swelling in all or part of a limb or another part of the body. Treatment for lymphedema depends on the severity and extent of the condition. Wounds may heal more slowly on the part of your body that has lymphedema.
For others the condition does worsen. Decongestive treatment is commonly recommended for the first two stages of. Once you have it your only options are to manage it to the best of your abilities or allow it to get out of control.
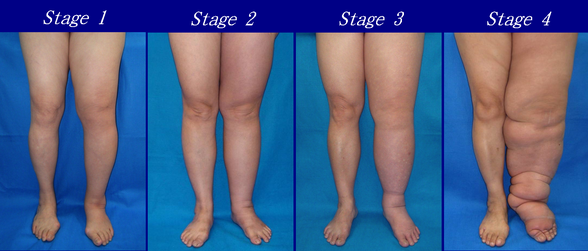
Lymphedema most often affects a single arm or leg but in uncommon situations both limbs are affected. This is often called the Reversible stage since the edema can reverse and go away with elevation or compression. Stage 2 - Moderate Stage.
Lymphedema is a build-up of lymph fluid in the fatty tissues just under your skin. The good news is that even if you have experienced some permanent damage you MAY still be able to reduce your level of excess fat to a point where your lymphedema goes away regardless. Lymphedema raises your risk of getting an infection in the swollen area.
Accumulation of protein-rich fluid with limb swelling that does not resolve with limb elevation. This build-up might also be called an obstruction and cause swelling and discomfort. The later stages of lymphedema often cant be completely reversed because the tissue under the skin has been damaged.
These treatments can help. It can be difficult to fit into clothes and jewellery and watches can feel tight. It often happens in the arms or legs but can also happen in the face neck trunk abdomen belly and genitals.
The lymphatic systems of some patients can no longer manage the fluid which builds up and collects in the arm or other areas of the body causing swelling and pain. Lymphedema can be managed with effective treatment but there is no cure. In other words lymphedema will not go away on its own but with time and treatment it gets better.
If you have lymphedema you can lose weight through exercise and healthy eating. There are several types of lymphedema. The most common type of lymphedema is painless and may slowly develop 18 to 24 months or more after surgery.
Exercise may improve circulation in your lymph system and reduce the swelling of your lymphedematous arm or leg even though lymphedema itself cannot be cured. When the lymph vessels are blocked or unable to carry lymph fluid away from the tissues localized swelling lymphedema is the result. Personally I dont wear the compression stockings as I.
As someone who has had lymphedema in the legs since I was 10 42 now and no it does not go away. There is no cure for lymphedema however it may go away on its own and there are treatments that you can do to help promote healing. A mild type of lymphedema can occur within a few days after surgery and usually lasts a short time.
Tiny round organs called nodes line the lymphatic system and trap toxins and foreign bodies such as bacteria. This happens because the cells that prevent infection cant reach that part of your body. At first the swelling may come and go.
You can keep it under control to whatever extent by avoiding standing for long periods of time. It may get worse during the day and go down overnight. You may feel upset depressed embarrassed or angry about the lymphedema.
The excess fluid in the lymph vessels is eventually returned to the bloodstream. There is early dermal fibrosis starting to develop. Edema refers to the swelling or buildup of excessive fluids.
Keep it up The only real way to know if obesity-related lymphedema has caused permanent damage to your lymphatics is to lose weight and see if your swelling goes away and stays away. Its important to know that lymphedema can sometimes become severe. Unfortunately ignoring lymphedema wont make it go away.