The material that obstructs urinary catheters consists of bacteria glycocalyx protein and precipitated crystals1 Patients who tend to develop blocked catheters excrete more calcium protein and. It may be necessary for a person to use a urinary catheter if they have difficulty passing urine naturally.
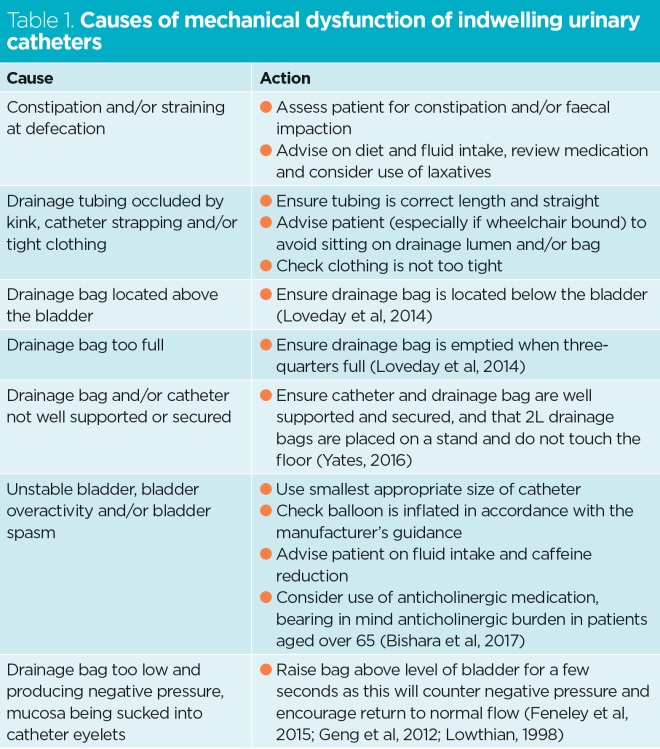 Using Patency Solutions To Manage Urinary Catheter Blockage Nursing Times
Using Patency Solutions To Manage Urinary Catheter Blockage Nursing Times
It may be greater in facilities that have poor success with toileting programs because the catheter is used as a means to maintain resident dryness.

Urinary catheter outcomes evaluation. Through evaluation by senior nursing leadership the Quality Improvement Project QIP was developed to create an organization structure that would be effective in implementing enterprise-wide evidence based practice EBP and ensure standard of care was being given in all areas to make an effective impact on lowering CAUTI rates. The protocol provided nurses with the decision support for assessment and discontinuation of indwelling urinary catheters. A urinary catheter is a flexible tube for draining urine from the bladder.
These infections are a reflection of the quality of hospital care provided to patients. The prevalence of indwelling urinary catheter use in nursing homes has been established as 5-7. Analysis was by intention-to-treat.
Middleton Memorial VA Hospital Madison WI 53705. An indwelling catheter is specifically defined as a drainage tube inserted into the urinary bladder through the urethra left in place and connected to a closed collection system. Known urethral stricture which in the opinion of the investigator could influence the subjects evaluation of.
Urinary catheterization is a common intervention used by home healthcare patients to manage urinary problems such as urinary retention and urinary incontinence. Outcome measures comprised of pre- and post-CAUTI data. As such it excludes straight catheters suprapubic catheters nephros-tomy tubes ileoconduits and condom catheters.
Focus group sessions were held to evaluate. The incidence of bacteriuria significant urinary tract infection and cost associated with the use of two urinary catheter drainage systems were evaluated in a population of hospitalized adult males. The definition of UTI is a positive urine culture of 103 CFUml of 1 bacterial species and presence of symptoms or signs compatible with UTI with no other identified source of infection.
The common use of this intervention does not however imply that catheterization is without serious complication or is always used appropriately. Outcome measures were the CAUTI National Healthcare Safety Network NHSN Standardized Infection Ratio SIR the number of CAUTIs per. The primary outcome was all-cause PIVC failure as a composite of occlusion infiltration dislodgement phlebitis and primary bloodstream or local infection.
The intervention group received education reinforcing practice guidelines including administration with manufacturer-prepared pre-filled flush syringes. The protocol provided nurses with the decision support for assessment and discontinuation of indwelling urinary catheters. Urinary catheters come in.
However there is no evidence that this process improves patient care. Urinary catheters come in many sizes and types. Implementation also included in-services.
A urinary catheter is a hollow partially flexible tube that collects urine from the bladder and leads to a drainage bag. This has been a common practice throughout a major southwestern hospital system. A prospective observational mixed methods study was used to evaluate outcomes from using MCs for blood withdrawal.
Drawing blood samples from short peripheral catheters is associated with higher hemolysis rates. POST REMOVAL PROCESS AND OUTCOME EVALUATION Evaluation of Interventions to Reduce Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infections. The purpose of this initiative is to reduce the use of indwelling urinary catheters as a routine intervention for patients in labor who have had an epidural.
Hospital acquired infections HAIs are a critical patient safety concern. With indwelling catheters in place for over 48 hours. Studies indicate that a patients perception and satisfaction of labor are improved.
Outcome measures comprised of pre- and post-CAUTI data. Implementation also included in-services.
