A CT pulmonary angiogram CTPA is the preferred method for diagnosis of a pulmonary embolism due to its easy administration and accuracy. Although a CTPA is preferred there are also other tests that can be done.
 Deep Venous Thrombosis And Pulmonary Embolism Diagnostic Approach A
Deep Venous Thrombosis And Pulmonary Embolism Diagnostic Approach A
It then travels to a lung artery where it suddenly blocks blood flow.

Pulmonary embolism labs. A pulmonary embolism is a blood clot in the lung that occurs when a clot in another part of the body often the leg or arm moves through the bloodstream and becomes lodged in the blood vessels of the lung. A pulmonary embolism is a blockage in the pulmonary artery which supplies the blood to the lungs. Integration of aggravating conditions and comorbidity into risk assessment of acute pulmonary embolism.
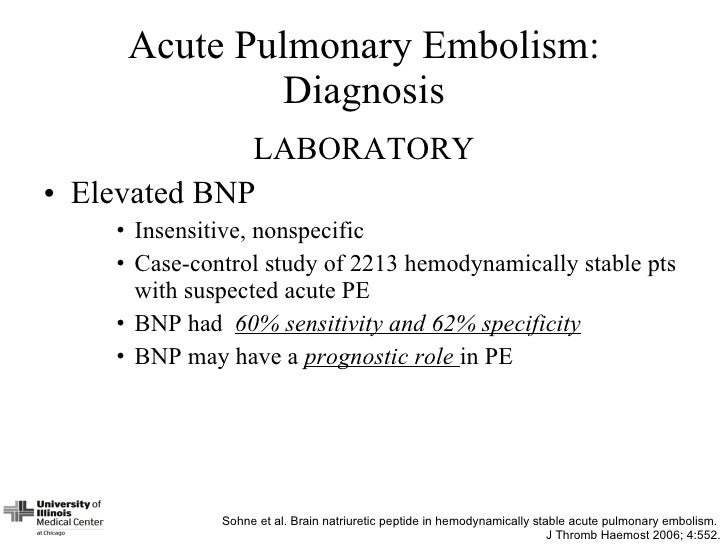
Combined parameters and scores for assessment of pulmonary embolism severity. The reason is normally a blood coagulation in the leg considered a profound vein thrombosis that loosens up and ventures out through the circulation system to the lung. Markers of myocardial injury.
An embolus can also be detected by the absence of sounds over part of the lung and changes on the ECG an electrical recording of. Pulmonary embolism often arises from a deep vein thrombosis and may have been previously overlooked. Risk factors for pulmonary embolism are conditions that impair venous return conditions that cause endothelial injury or.
Monitor for any changes in the ABGs. To provide a diagnostic approach to patients with suspected acute pulmonary embolism PE. A pulmonary embolism PE is a blood clot that develops in a blood vessel in the body often in the leg.
These laboratory studies can be obtained to rule out other cause of chest discomfort and tachypnea. Here are some lab tests that you may be required. Although pulmonary embolism can arise from anywhere in the body most commonly it arises from the calf veins.
Pulmonary embolism is the occlusion of pulmonary arteries by thrombi that originate elsewhere typically in the large veins of the legs or pelvis. A large pulmonary embolus blocks off a major portion of one lung with resulting sudden severe breathlessness faintness chest pain and often coughing of blood. The results of routine laboratory tests including arterial blood gas analysis are non-specific in making the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism PE.
However all imaging techniques have their own limitations and costs and cannot be performed in every patient with suspected PE. Chest X-ray can provide images of your lungs heart blood vessels airways and the bones of the chest and spine. The diagnosis of pulmonary embolism PE requires objective testing.
A blood clot that forms in a blood vessel in one area of the body breaks off and travels to another area. This is usually non-invasive and this can help your doctor diagnose and treat pulmonary embolism in. The venous thrombi predominately originate.
A large pulmonary embolus or multiple small clots in a specific area of the lung can cause ischemic necrosis or infarction of the lung area. These patients usually lack any other classical signs symptoms or known risk factors for pulmonary thromboembolism. Venous thromboembolism VTE which comprises deep vein thrombosis DVT and pulmonary embolism PE is a common disease affecting approximately 1-2 in 1000 adults per year.
This restricts blood flow to the lungs lowers oxygen levels in the lungs and increases blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries. Computed tomographic pulmonary angiography. Pneumonic embolism is a genuine condition that can cause.
After decades of unfruitful research several laboratory tests have been evaluated for suspected PE the most promising being the D-dimer test. Assess for calf tenderness redness swelling and hardened areas. Markers of right ventricular dysfunction.
Such patients often are dismissed inappropriately with an inadequate workup. For example a proximal lower limb compression ultrasound CUS can be used. The pathophysiology of pulmonary embolism.
A pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot that has developed elsewhere in your body often in your arm or leg travels through your bloodstream to your lungs and becomes stuck in. Pulmonary embolism has been diagnosed in 21 of young active patients who come to emergency departments EDs complaining only of pleuritic chest pain.
