Venous Thromboembolism Prevention Clinical Care Standard was developed by the Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care the Commission in collaboration with consumers clinicians researchers and health service organisations. The initial treatment for venous thromboembolism is typically with either low-molecular-weight heparin LMWH or unfractionated heparin or increasingly with directly acting oral anticoagulants DOAC.
 Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis May Cause More Harm Than Benefit An Evidence Based Analysis Of Canadian And International Guidelines Thrombosis Journal Full Text
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis May Cause More Harm Than Benefit An Evidence Based Analysis Of Canadian And International Guidelines Thrombosis Journal Full Text
Venous thromboembolism VTE encompassing both deep vein thrombosis DVT and pulmonary embolism PE is the most common cause of preventable in-hospital death 12.

Venous thromboembolism prevention. Surgical procedures may also be used. Among people who have had a DVT one third to one half will have long-term complications post-thrombotic syndrome such as swelling pain discoloration and scaling in the affected limb. The two primary methods of VTE prevention in use today are mechanical compression and pharmacological thromboprophylaxis.
Grade 1 recommendations are strong and indicate that the benefits do or do not outweigh risks burden and costs. This article discusses the prevention of venous thromboembolism VTE and is part of the Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy. Anticoagulant and thrombolytic therapy options are available for the treatment of venous thromboembolism VTE.
This article discusses the prevention of venous thromboembolism VTE and is part of the Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy. Enous thromboembolism VTE prevention is addressed daily in nearly every hospital in the world. Venous Thromboembolism Prevention.
38 Unfractionated heparin UFH. Pharmacologic options for VTE treatment and prevention include unfractionated heparin UFH low-molecular-weight heparins LMWHs fondaparinux an indirect synthetic inhibitor of activated factor Xa vitamin K antagonists VKAs and direct oral anticoagulants DOACs. Grade 2 suggestions imply that individual.
One particular area of controversy that I have repeatedly encountered over the last two decades is the use of early post spinal surgical VTE prophylaxis. Patient may have multiple risk factors that are offset. Venous thromboembolism is a common complication for patients suffering from a spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage ICH 1 2.
Grade 1 recommendations are strong and indicate that the benefits do or do not outweigh risks burden and costs. Venous Thromboembolism VTE Prevention Inpatient Inclusion Criteria. The Venous Thromboembolism Prevention Clinical Care Standard has been developed by the Commission to support clinicians and health services implement the delivery of high-quality care to prevent venous thromboembolism VTE acquired in hospital and following hospital discharge.
It complements existing efforts including state and territory-based initiatives. Anticoagulant therapy prevents further clot deposition and allows the patients. Previously known as novel oral anticoagulants including direct thrombin inhibitors and direct factor Xa inhibitors.
Patients in the NICU Patients in the MFCU Patients with current VTE. American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines 8th Edition. All inpatients with anticipated hospitalization greater than 23 hours Exclusion Criteria.
This can be given through an arm vein and also by inserting catheters directly into the blood clot in the vein or lung. One-third about 33 of people with DVTPE will have a recurrence within 10 years. Meta-analyses have demonstrated that pharmacologic VTE prophylaxis reduces the risk of symptomatic DVT PE and fatal PE by approximately 50 at the expense of a modest increase in major bleeding.
Thrombolytic therapy which includes drugs such as a tissue plasminogen activator tPA a clot-dissolving enzyme. The 2 primary modalities of VTE prophylaxis are mechanical eg graduated compression stockings intermittent pneumatic compression sequential compression devices and foot pumps and pharmacologic unfractionated heparin or low-molecular-weight heparin LMWH. DVT and PE comprise venous thromboembolism VTE.
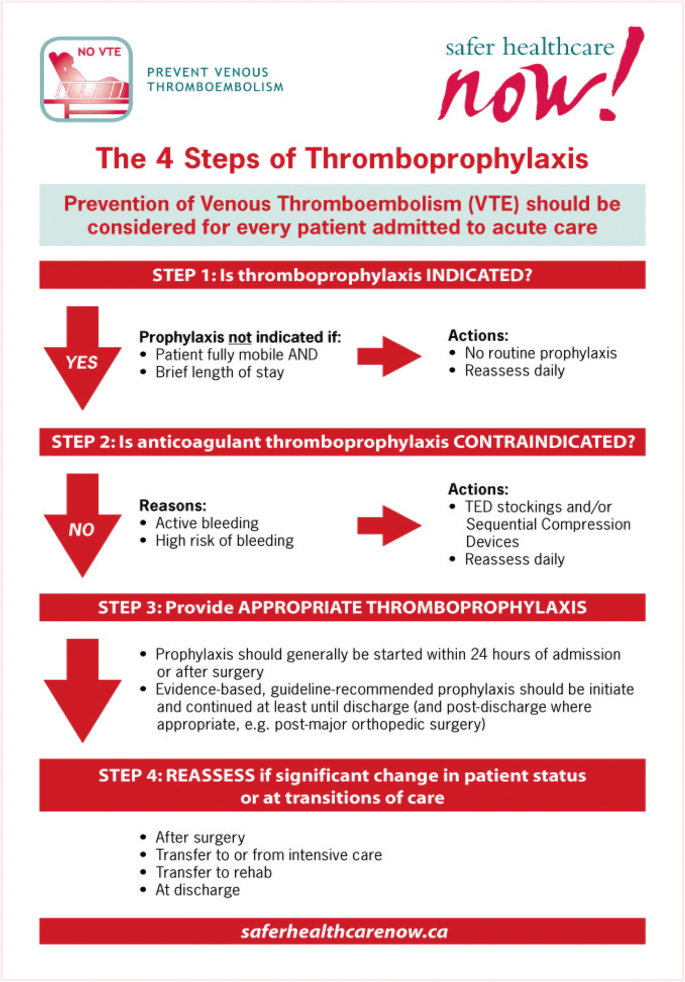
To participate in this study you must be at least 18 years old and must not have been diagnosed with VTE in the last two years. VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM VTE PREVENTION ALGORITHM. American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines 8th Edition.
This study will assess a medicine called isoquercetin to see if it can prevent a venous thromboembolism VTE in patients getting treatment for pancreatic colorectal and non-small cell lung cancer.
.jpg)

/thyroid-cancer-causes-5b2bc5383037130037637cc0.png)


