Stallone RJ Iverson LI Young JN. Aneurysm of the thoracic aorta is less common than in the abdominal aorta but it is clinically important because of the risk of rupture and death.
 Ascending Aortic Aneurysm Repair Surgery And Size Criteria
Ascending Aortic Aneurysm Repair Surgery And Size Criteria
A 10 year surgical experience.
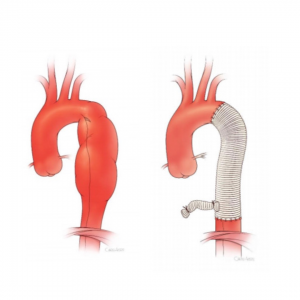
Descending thoracic aortic aneurysm. A descending thoracic aortic aneurysm is a bulging weakened area in the wall of the aorta in the part that runs downward through the chest thorax. Type A descending thoracic aortic aneurysms left subclavian artery to T6 were repaired in 42 patients 284 type B T6 to the diaphragm in 24 patients 162 and type C left subclavian artery to the diaphragm in 82 patients 554. Aorta is the biggest blood vessel of humans and it is responsible to deliver blood from a persons heart to various other parts of the body.
Aneurysms that involve the aorta as it flows through both the abdomen and chest are called thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms. Descending thoracic aortic aneurysms were classified according to Figure 3. Aneurysms involving the descending and abdominal aorta are classified as thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms.
Approximately 60 of TAAs occur in the root or ascending aorta 10 in the arch 40 in the descending aorta and 10 in the thoracoabdominal aorta with some aneurysms involving multiple aortic segments. Descending type of thoracic aortic aneurysm refers to weakness and bulging in the wall of a descending thoracic aorta ie. Most patients are asymptomatic for a long period of time until the thoracic aortic disease is very advanced or found incidentally on a.
We report our experience with extensive TAAs using a two-stage elephant trunk repair with the second stage completed using an endovascular stent graft ESG. Cases are often found incidentally. A descending thoracic aortic aneurysm is bulging and weakness in the wall of the descending thoracic aorta located in the back of the chest cavity.
The anatomy of the descending aorta makes it more favorable for endovascular approaches in some cases however more complex problems will still require open surgery. Sudden severe pain associated with a thoracic aneurysm may be a sign of a life-threatening medical emergency. When symptoms do occur they may be related to the location size and how fast the aneurysm is growing.
Descending thoracic aortic aneurysms are the third most common aortic aneurysm. Aortic aneurysms that occur in the chest area are called thoracic aortic aneurysms and can involve the aortic root ascending aorta aortic arch or descending aorta. The advantages are minimal blood loss due to the absence of heparin ease of insertion especially in large aneurysms where it.
A thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm is one that is located in the area where the aorta crosses between the chest and abdomen. The artery remains present in the back portion of individuals chest cavity. The aorta is the largest blood vessel in the body and it delivers blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
Descending thoracic aortic aneurysm. 3 Multiple factors rather than a single process are implicated in the pathogenesis of TAA. Reconstruction of aortic arch and descending thoracic aortic aneurysms TAAs is technically challenging and associated with significant morbidity and mortality.
Since the advent of endovascular techniques for repair of descending thoracic aortic aneurysms DTAAs there has been a relative paucity of current data for open repairs. The descending aorta provides important blood flow to the spinal cord. Pain in the jaw.
Presently we favor heparinless femorofemoral venoarterial bypass for all descending thoracic aneurysm resections. What are the symptoms of a thoracic aortic aneurysm. Symptoms of a thoracic aneurysm may include.
Thoracic aortic aneurysms may not cause symptoms. The purpose of this study was to assess the operative and long-term outcomes in a contemporary series of open repairs of DTAAs. The majority of patients are diagnosed in their 6th and 7th decade of life.


